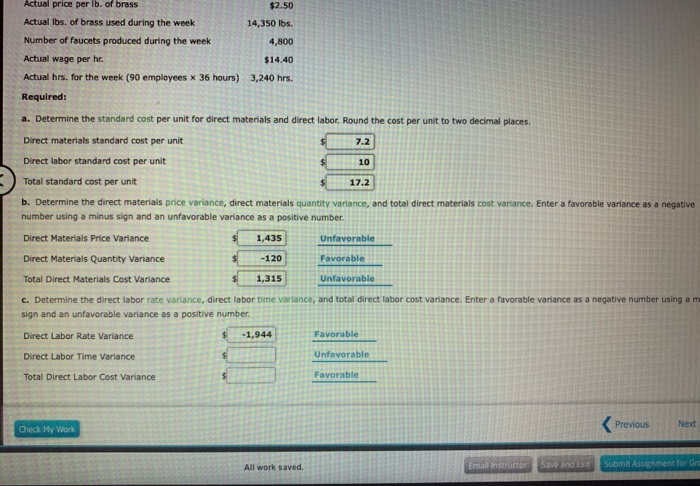
On the other hand, if workers use the quantity that is more than the quantity allowed by standards, the variance is known as unfavorable direct materials quantity variance. The standard cost of actual quantity purchased is calculated by multiplying the standard price with the actual quantity. This amount will represent the expected expenditure on direct material for this many units.
How to Calculate Material Price Variance
We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
Direct Materials Price Variance
If the budget variance is positive, you can see where the efficiencies or cost savings lie. If the budget variance is negative, then you know which areas need improvement. Managers can better address this situation if they have a breakdown of the variances between quantity and price.
Formula For Direct Materials Quantity Variance
Effective management of direct material variance can lead to significant savings and better resource allocation. It also helps identify inefficiencies within the supply chain or production process that may otherwise go unnoticed. The standard price of $100 per bag was allowed in the budget, but the purchase manager was able to source the materials from a cheaper supplier at the cost of $80 per bag. Ideally, as a small business owner, you would hope a financial analysis will result in a favorable or positive variance, meaning you are not exceeding your budget. However, that does not mean a negative variance may be unexpected for your quarter or year end. Perhaps sales have been suffering lately and your product is piling up and you need a new plan.
- Variances occur in most of the manufacturing processes and for almost all cost elements.
- For example, the unfavorable price variance at Jerry’sIce Cream might have been a result of purchasing high-qualitymaterials, which in turn led to less waste in production and afavorable quantity variance.
- The following equations summarize the calculations for direct materials cost variance.
It evaluates the extent to which the standard price has been over or under applied to different units of purchase. Actual and standard quantities and prices are given in the following table for direct full charge bookkeeper alternative careers and similar jobs updated for 2023 materials to produce 1,000 units. Total actual and standard direct materials costs are calculated by multiplying quantity by price, and the results are shown in the last row of the first two columns.
How is direct materials price variance calculated?
You had budgeted for materials, labor and manufacturing supplies at the outset. With direct labor costs in particular you had calculated twenty hours for one blanket to be produced, but it’s averaging a total of fifteen, meaning the difference between the actual and budgeted amount is five hours. Note that both approaches—the direct materials price variancecalculation and the alternative calculation—yield the sameresult.
Standard costs are used to establish theflexible budget for direct materials. The flexible budget iscompared to actual costs, and the difference is shown in the formof two variances. The materials quantity variancefocuses on the quantity of materials used in production. It isdefined as the difference between the actual quantity of materialsused in production and budgeted materials that should have beenused in production based on the standards.
In such cases, the responsibility of any unfavorable quantity variance would lie on the purchasing department. Irrespective of who appears to be responsible at first glance, the variance should be brought to the attention of concerned managers for quick and timely remedial actions. In this case, the actual price per unit of materials is $9.00, the standard price per unit of materials is $7.00, and the actual quantity used is 0.25 pounds. This is an unfavorable outcome because the actual price for materials was more than the standard price.